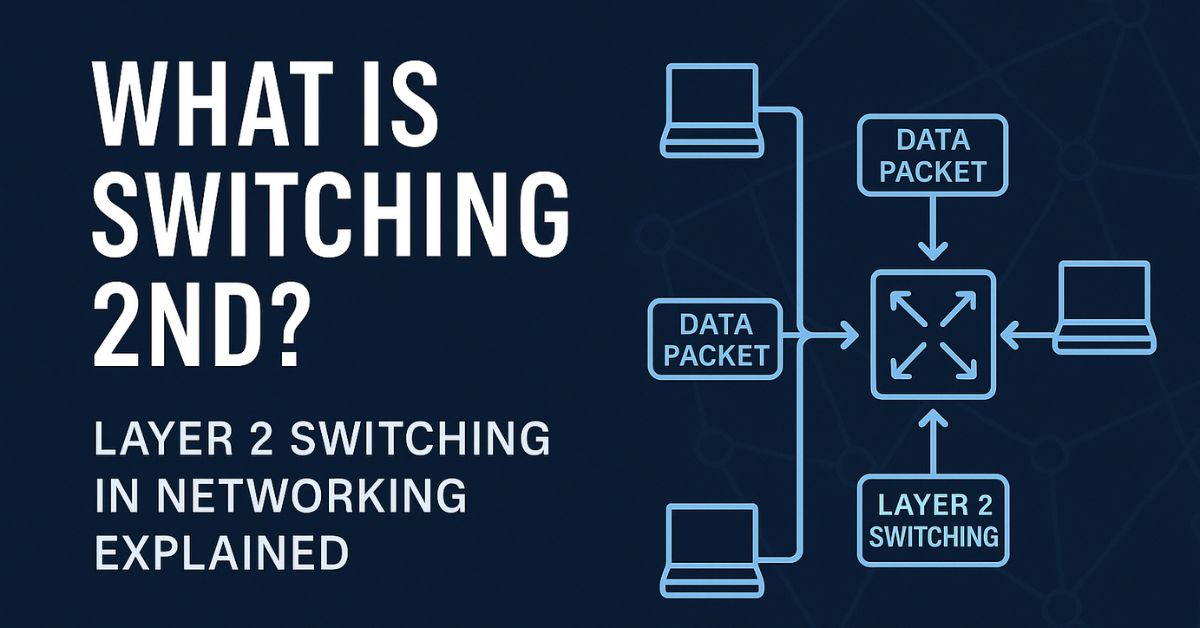
Switching in networking plays a fundamental role in how data moves within a local area network (LAN). Specifically, Layer 2 switching, also referred to as Data Link layer switching, is a lightning-fast technique for forwarding data frames based on MAC addresses.
In this blog, we’ll decode what switching means in networking, explain how Layer 2 switches work, and explore why this method is a crucial pillar of modern IT infrastructure. This article is powered by NLP-focused language and rich LSI keywords to help you understand and rank better if you’re learning or blogging about networking. The C9200 is a reliable and secure enterprise-grade switch designed for modern network infrastructures.
What is Switching in Networking?
Switching is the process of transferring data packets between devices on a network by analyzing destination information. It ensures that your file transfers, video calls, and internet activity reach the intended device, fast and reliably.
There are different types of switching:
Circuit Switching
Packet Switching
Message Switching
But in this article, we focus on the most relevant in LAN environments—Layer 2 Switching.
Layer 2 Switching – Fast, Efficient, Reliable
Layer 2 switching takes place at the Data Link Layer (second layer of the OSI model). It uses the MAC address, a unique hardware identifier, to forward packets from one device to another without involving IP addresses.
How it works:
When a data frame enters a Layer 2 switch, it reads the destination MAC address, checks its MAC address table, and instantly forwards the frame out the correct port. This action is:
Hardware-based
Low latency
Doesn’t require routing logic
No need for IP lookups or subnetting
High-speed forwarding for LANs
Reduces broadcast traffic
Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switching
| Feature | Layer 2 Switching | Layer 3 Switching |
|---|---|---|
| Works on | Data Link Layer (L2) | Network Layer (L3) |
| Uses | MAC addresses | IP addresses |
| Speed | Faster (no IP processing) | Slower (routing logic involved) |
| Devices used | Ethernet Switch | Layer 3 Switch / Router |
| Use-case | LAN switching | Inter-VLAN routing, WAN traffic |
| Configuration | Plug-and-play | Requires routing tables |
Why Layer 2 Switching is Crucial
Low Latency: Eliminates the need for CPU-intensive IP processing
Scalable: Easy to deploy in enterprise networks or home setups
Secure: Advanced switches support VLANs, port security, and QoS
Plug-and-play: Works automatically once devices are connected
Real-World Applications of Layer 2 Switching
Layer 2 switching is used in:
Office networks (to connect computers, printers, VoIP phones)
Home Wi-Fi routers with Ethernet ports
Smart buildings and IoT hubs
Data centers for fast internal communication
Gaming setups for ultra-low ping transmission
Final Thoughts
Layer 2 switching isn’t just an old-school term—it’s still the backbone of fast and efficient networks. Whether you’re building a small office network or managing a high-performance enterprise LAN, mastering the concept of switching at Layer 2 can unlock better speed, performance, and control.